Types of Computer (कंप्यूटर के प्रकार )
We can categorize computer by two ways: data handling capabilities and size.
On the basis of data handling capabilities, the computer is of three types:
- Analogue Computer(एनालॉग कंप्यूटर )
- Digital Computer (डिजिटल कंप्यूटर )
- Hybrid Computer (हाइब्रिड कंप्यूटर )
1) Analogue Computer(एनालॉग कंप्यूटर )
Analog computers are designed to process analogue data. Analogue data is continuous data that changes continuously and cannot have discrete values such as speed, temperature, pressure and current.
The analogue computers measure the continuous changes in physical quantity and generally render output as a reading on a dial or scale.
Analogue computers directly accept the data from the measuring device without first converting it into numbers and codes.
Speedometer and mercury thermometer are examples of analogue computers.
2) Digital Computer(डिजिटल कंप्यूटर)
A digital computer is designed to perform calculations and logical operations at high speed. It accepts the raw data as digits or numbers and processes it with programs stored in its memory to produce output. All modern computers like laptops and desktops that we use at home or office are digital computers.
3) Hybrid Computer(हाइब्रिड कंप्यूटर )
A hybrid computer has features of both analogue and digital computer. It is fast like analogue computer and has memory and accuracy like digital computers. It can process both continuous and discrete data. So it is widely used in specialized applications where both analogue and digital data is processed. For example, a processor is used in petrol pumps that converts the measurements of fuel flow into quantity and price.
On the basis of size, We can Divide into 5 Parts.
1) Supercomputer (सुपर कंप्यूटर )
Supercomputers are the biggest and fastest computers. They are designed to process huge amount of data. A supercomputer can process trillions of instructions in a second. It has thousands of interconnected processors.
Supercomputers are particularly used in scientific and engineering applications such as weather forecasting, scientific simulations, and nuclear energy research. The first supercomputer was developed by Roger Cray in 1976.
2) Mainframe computer (मेनफ़्रेम कंप्यूटर )
Mainframe computers are designed to support hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously. They can support multiple programs at the same time. It means they can execute different processes simultaneously. These features of mainframe computers make them ideal for big organizations like banking and telecom sectors, which need to manage and process high volume of data.
3) Miniframe computer (मिनिफ़्रेम कंप्यूटर )
It is a midsize multiprocessing computer. It consists of two or more processors and can support 4 to 200 users at one time. Miniframe computers are used in institutes and departments for the tasks such as billing, accounting and inventory management.
4) Workstation (वर्कस्टेशन )
Workstation is a single user computer that is designed for technical or scientific applications. It has faster microprocessor, large amount of RAM and high speed graphic adapters. It generally performs a specific job with great expertise; accordingly, they are of different types such as graphics workstation, music workstation and engineering design workstation.
5) Microcomputer (मइक्रोकम्प्युटर )
Microcomputer is also known as personal computer. It is a general purpose computer that is designed for individual use. It has a microprocessor as a central processing unit, memory, storage area, input unit and output unit. Laptops and desktop computers are examples of microcomputers.
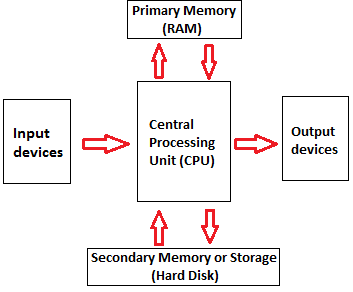
Computer Components(It's a very Important)
There are 5 main computer components that are given below:
- Input Devices (इनपुट डिवाइस )
- CPU (सेंट्रल प्रोसेसिंग यूनिट )
- Output Devices (आउटपुट यूनिट )
- Primary Memory (प्राइमरी यूनिट )
- Secondary Memory (सेकेंडरी यूनिट )
The operations of computer components are given below:
1) Inputting: It is the process of entering raw data, instructions and information into the computer. It is performed with the help of input devices.
2) Storing: The computer has primary memory and secondary storage to store data and instructions. It stores the data before sending it to CPU for processing and also stores the processed data before displaying it as output
.
3) Processing: It is the process of converting the raw data into useful information. This process is performed by the CPU of the computer. It takes the raw data from storage, processes it and then sends back the processed data to storage.
4) Outputting: It is the process of presenting the processed data through output devices like monitor, printer and speakers.
5) Controlling: This operation is performed by the control unit that is part of CPU. The control unit ensures that all basic operations are executed in a right manner and sequence.
Comments
Post a Comment