Memory Hierarchy
A memory unit is an essential component in any digital computer since it is needed for storing programs and data.
Typically, a memory unit can be classified into two categories:
- The memory unit that establishes direct communication with the CPU is called Main Memory. The main memory is often referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory).
- The memory units that provide backup storage are called Auxiliary Memory. For instance, magnetic disks and magnetic tapes are the most commonly used auxiliary memories.
Apart from the basic classifications of a memory unit, the memory hierarchy consists all of the storage devices available in a computer system ranging from the slow but high-capacity auxiliary memory to relatively faster main memory.
The following image illustrates the components in a typical memory hierarchy.
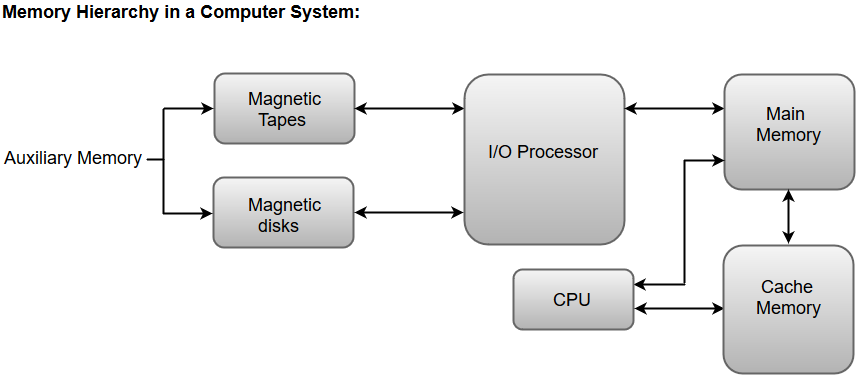
Auxiliary Memory
Auxiliary memory is known as the lowest-cost, highest-capacity and slowest-access storage in a computer system. Auxiliary memory provides storage for programs and data that are kept for long-term storage or when not in immediate use. The most common examples of auxiliary memories are magnetic tapes and magnetic disks.
A magnetic disk is a digital computer memory that uses a magnetization process to write, rewrite and access data. For example, hard drives, zip disks, and floppy disks.
Magnetic tape is a storage medium that allows for data archiving, collection, and backup for different kinds of data.
Main Memory
The main memory in a computer system is often referred to as Random Access Memory (RAM). This memory unit communicates directly with the CPU and with auxiliary memory devices through an I/O processor.
The programs that are not currently required in the main memory are transferred into auxiliary memory to provide space for currently used programs and data.
I/O Processor
The primary function of an I/O Processor is to manage the data transfers between auxiliary memories and the main memory.
Cache Memory
The data or contents of the main memory that are used frequently by CPU are stored in the cache memory so that the processor can easily access that data in a shorter time. Whenever the CPU requires accessing memory, it first checks the required data into the cache memory. If the data is found in the cache memory, it is read from the fast memory. Otherwise, the CPU moves onto the main memory for the required data.
We will discuss each component of the memory hierarchy in more detail later in this chapter.
You really explain things with clarity
ReplyDelete